pleural effusion cat symptoms
Cirrhosis or poor liver function. Fluid color Ascites pleural effusion Yellow Yellow-green Light yellow Deep yellow Milk-white Blood-red.
The breathing pattern of your cat will be examined as well as the chest auscultated.
. The most common causes for pleural effusion in all 380 cats were found to be CHF n155 408 and neoplasia n98 258. The second most common cause of pericardial effusion in cats is cancer including tumors of the heart or pericardium. Cats with pleural effusion often have rapid shallow breathing and pet owners may.
When this distress is sufficiently acute it can. It can cause breathing difficulties which may be mild to severe depending upon how much fluid has built up and what other problems if any are involved. Treatment for feline lymphoma is also usually successful in the short-term with remission rates approaching 75 percent.
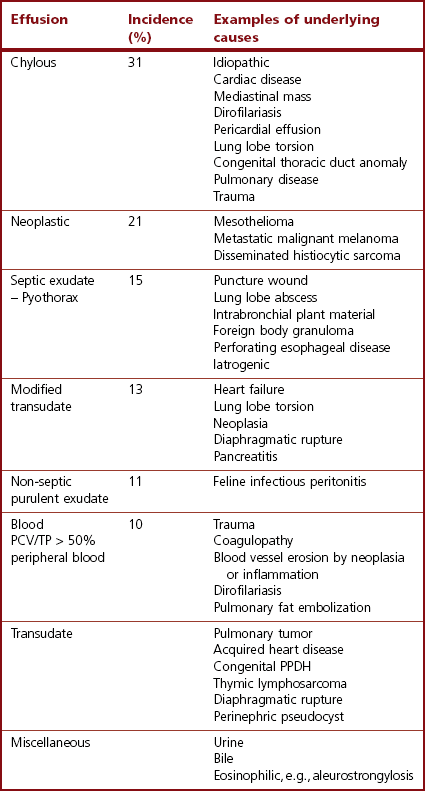
Eighty-two cases of feline pleural effusion were identified and reviewed to assess the type of fluid underlying disease process predisposing conditions historical and physical examination findings laboratory and cytology data response to treatment and outcome. Transudate protein poorclear watery fluid effusion or exudate protein-richthick. The most commonly diagnosed cause of pleural effusion in cats is chylothorax.
Pleural effusion sometimes called water on the lungs is a build-up of fluid in the space that surrounds your cats lungs. Pleural effusion itself is typically fairly easy to treat and the short-term prognosis is usually good. Pulmonary embolism which is caused by a blood clot and is a blockage in the lung.
The clinical signs of pleural effusion in the cat are generally as follows. Pericardial effusion may also be idiopathic with no known diagnosable cause. Careful handling and prompt and adequate stabilisation incorporating supplemental oxygen and therapeutic thoracocentesis is essential to avoid respiratory failure.
The typical stepwise approach to the case must be adapted and the. Please be noted that both form of FIP are interchangeable cats may show symptoms from both form at the same time. Mediastinal lymphoma in cats with feline leukemia carries a poor prognosis with an average survival time of 3 months.
If your cat is stable x-rays of the chest will be taken. Careful handling and prompt and adequate stabilisation incorporating supplemental oxygen. The best thing for treating this illness is to get rid of the fluid to restore free-breathing.
Cats with pleural effusion often have severe respiratory compromise at presentation. Most fluids can be classified as transudates or exudates. For more information about Cough in cats symptoms causes and treatment read this post that we suggest.
In acute cases cats may need supplemental oxygen until the pressure on their lungs is reduced. Typically this period of remission lasts only 2-9 months and then cats become ill again. Pleural effusion is a symptom of many diseases but is rarely a disease itself.
In human medicine increased RBCp 100000μl is associated with neoplastic effusion20 and also with trauma and pulmonary embolism24 and in a veterinary article an RBCp 50000μl was said to be associated in the absence of trauma with malignancy37 In our study no effusion was caused by trauma or pulmonary embolism and neoplastic. Its vital to see a vet the moment you notice any symptoms. Pleural effusion is a symptom with an underlying disorder causing this fluid to build up.
Pertinent findings included a high occurrence of pleural effusion with. Pleural effusion will usually make the lung sounds very difficult to hear with the stethoscope as the fluid interferes with the sound acoustics. Many cats which develop pleural effusion have severe difficulty breathing and can deteriorate rapidly.
Dyspnea or respiratory distress. Reduced lung sounds due to fluid. Asbestos pleural effusion due to exposure to asbestos Meigs syndrome due to a benign ovarian tumor Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Therefore most symptoms indicate that the feline has to work harder than before to get oxygen. Diagnostic tests are needed to determine the underlying cause and subsequent treatment recommendations are based on these findings. Cats with pleural effusion often have severe respiratory compromise at presentation.
As indicated by the VCA Hospitals portal pleural effusion in cats reduces the amount of space available for the expansion of the lungs in the chest when breathing. An abnormal build up of pleural fluid can cause the cat respiratory distress. Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity.
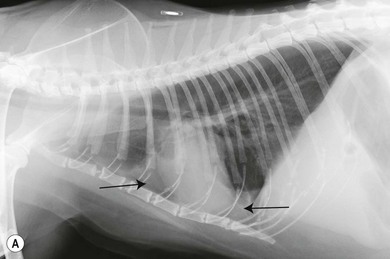
Chest x-rays can be used to detect pleural effusion. Other causes included pyothorax idiopathic chylothorax trauma FIP nontraumatic diaphragmatic hernia vasculopathy uremic pleuritis hypoproteinemia and vitamin K antagonist toxicity. Causes of pleural effusion include.
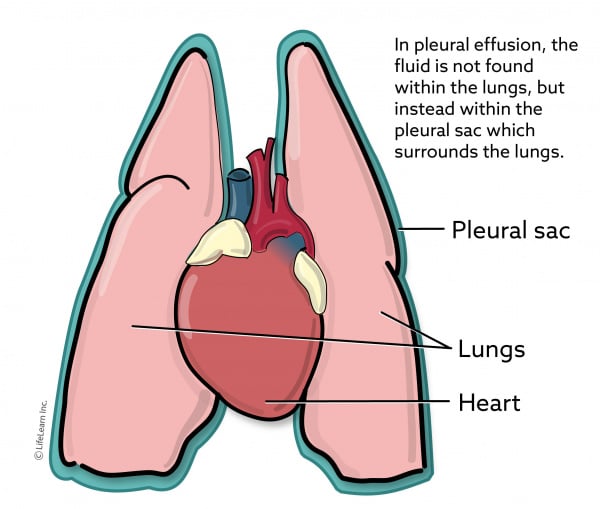
Less commonly pericardial effusion in cats may be caused by an infection or a birth defect known as a peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernia. Other less common causes of pleural effusion include. In pleural effusion the fluid is not found within the lungs but instead within the pleural sac.
This can be caused by thoracic lymphangiectasia swollen lymph vessels that leak chyle into the pleural space congestive heart failure obstruction of the cranial vena cava the major vein that returns blood to the heart from the front of the body cancer fungal. A cat abdominal breathing is life-threatening and an emergency for the cat. Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity the space between the pleural sacs of each lung.
There is some fluid naturally in this cavity but when fluid builds up it poses serious health risks. The buildup of excess fluid leads to difficulty breathing due to the inability of the lungs to fully expand. In cats without feline leukemia mediastinal lymphoma often shows at least a partial response to chemotherapy.
Wet FIP Cats with ascites or pleural effusion less than 2 years old and more than 8 years are highly suspected. Bleeding due to chest trauma Chylothorax due to trauma Rare chest and abdominal infections. Below is an overview of pleural effusion in cats followed by in-depth information on the diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Increased respiratory rate or tachypnea. Among the possible clinical signs we highlight the following. Pleural effusion can have a number of different causes including diseases of the heart lungs or other systemic diseases.

Fluid In Chest Pleural Effusion In Cats Petmd

Lateral Thoracic Radiograph Image Of A Cat With Pleural Effusion Due To Download Scientific Diagram
Congestive Heart Failure Catwatch Newsletter

Feline Xray Pleural Effusion Long Beach Animal Hospital

The Dyspneic Cat Is It The Heart Or Lower Airways Feline Dyspnea Respiratory Distress In Cats

Diagnostika Fip Fip Warriors Cz Sk

The Dyspneic Cat Is It The Heart Or Lower Airways Feline Dyspnea Respiratory Distress In Cats

Read About Emergency Medicine In This Article By Brigitte Brisson And More

Left Sided Congestive Heart Failure Clinician S Brief

Pleural Effusion In Cats Causes Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
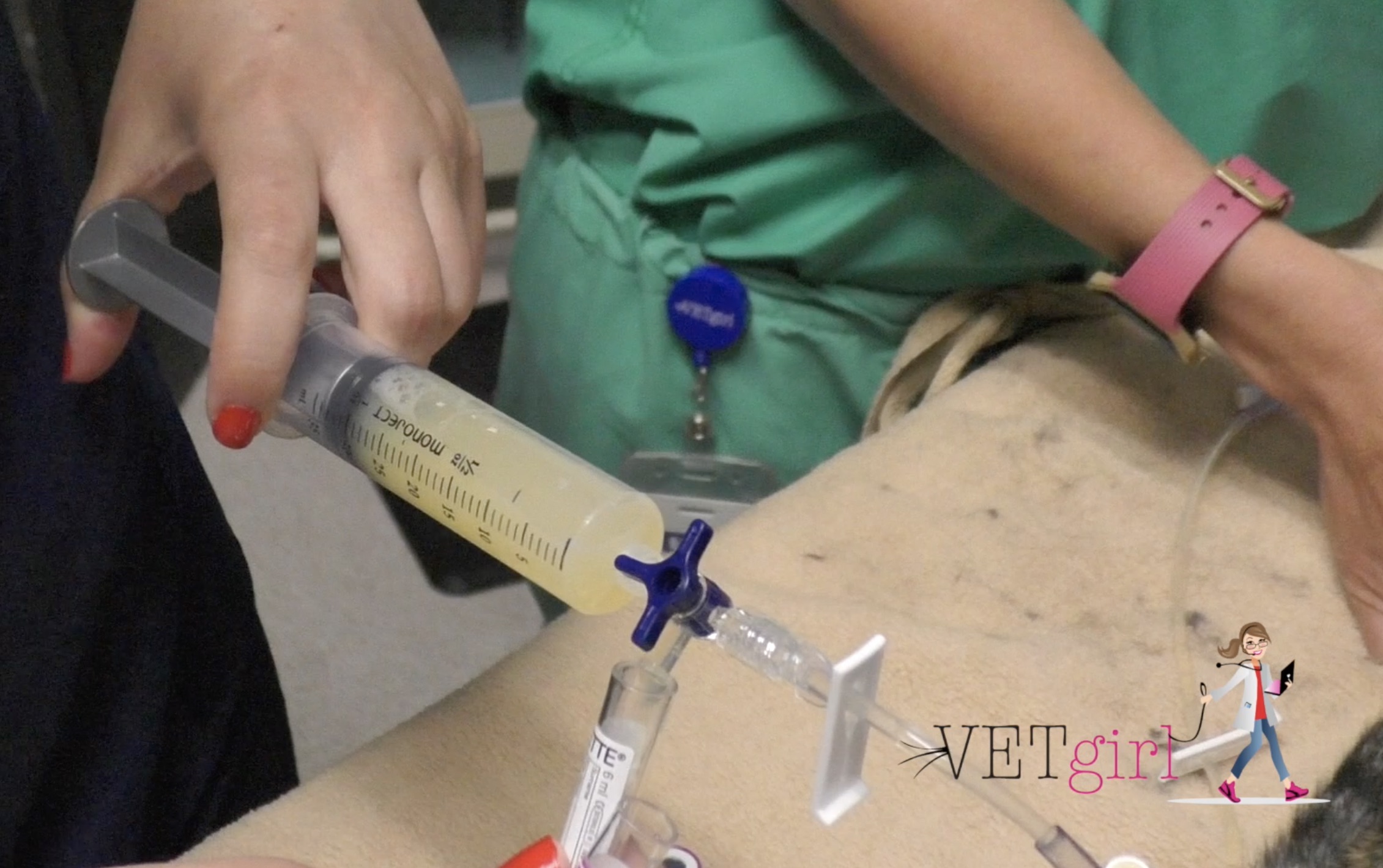
Causes Of Pleural Effusion In Cats Vetgirl Veterinary Continuing Education Blog
Pleural Effusion In Cats Vca Animal Hospital

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association

Spontaneous Cholecystopleural Fistula Leading To Biliothorax And Sepsis In A Cat

Reasons For Heavy Breathing In Cats And How To Help Lovetoknow